Some notes from this excellent video by Gayle McDowell on trees.
What is a binary tree?
A binary tree is a data structure where by each node has no more than two child nodes.

What is a binary search tree?
A binary search tree is a binary tree sorted in a specific ordering property. On any subtree, the left nodes are less than the root node, which is less than all of the right nodes.
This ordering makes finding a node really fast because we have pretty good idea of which way to go as we search the tree, going left or right and essentially halving our search area every step of the way.

Inserts
Insert works much like a find. We start at the top, do a comparison, and then head down to the child subtree and repeat the process again until we get down to an empty spot or null element.
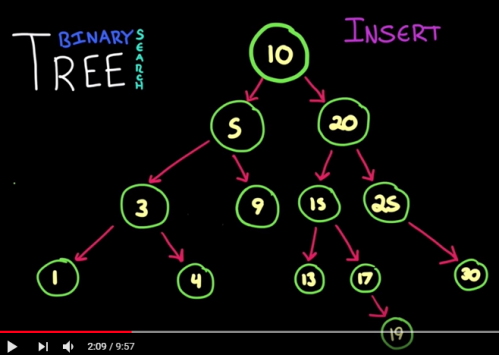
Note the one problem with this approach is that if we get elements in a particular order we can get really unbalanced.

And this will make our find ands inserts slow.
There are algorithms that you can use to keep a binary tree balanced, but they are pretty complicated, and in an interview you can generally assume that you are going to have a balanced tree.
Traversinge
There are three common ways we walk through a tree.
Preorder traversal: Means you visit the root of the tree first, and then you visit it’s left nodes and it’s right nodes. Top-bottom, left to right.
Inorder traversal: Left nodes first, then right. So left, parent, then right.
Post order: Left, then right, then root.

Typically in binary search trees we walk to do inorder traversal because that actually allows the nodes to be printed out in order.

Code for Binary Search Tree
NodeBST.java
public class NodeBST {
NodeBST left, right;
int data;
public NodeBST(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public void insert(int value) {
// look to the left and the right to see where we want to insert
if (value <= data) {
if (left == null) {
left = new NodeBST(value);
} else {
// push down to child and ask it to handle : recursion
left.insert(value);
}
} else {
if (right == null) {
right = new NodeBST(value);
} else {
right.insert(value);
}
}
}
public boolean contains(int value) {
// if we are there, return true
if (value == data) {
return true;
} else if (value < data) {
// then it should be on the left
// if there is no left node
if (left == null) {
return false;
} else {
return left.contains(value);
}
} else {
if (right == null) {
return false;
} else {
return right.contains(value);
}
}
}
// left child -> parent -> right child
public void printInOrder() {
if (left != null) {
left.printInOrder();
}
System.out.println("data = " + data);
if (right != null) {
right.printInOrder();
}
}
}
NodeBSTTest.java
import junit.framework.Assert;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
public class NodeBSTTest {
private NodeBST node;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
node = new NodeBST(10);
node.insert(5);
node.insert(15);
node.insert(8);
}
@Test
public void Contains() throws Exception {
Assert.assertTrue(node.contains(5));
Assert.assertTrue(node.contains(15));
Assert.assertTrue(node.contains(8));
}
@Test
public void PrintOrder() throws Exception {
node.printInOrder();
}
}

























Leave a comment